this post was submitted on 10 Apr 2025
1250 points (99.6% liked)
[Dormant] moved to !space@mander.xyz
11382 readers
1 users here now
This community is dormant, please find us at !space@mander.xyz
You can find the original sidebar contents below:
Rules
- Be respectful and inclusive.
- No harassment, hate speech, or trolling.
- Engage in constructive discussions.
- Share relevant content.
- Follow guidelines and moderators' instructions.
- Use appropriate language and tone.
- Report violations.
- Foster a continuous learning environment.
Picture of the Day
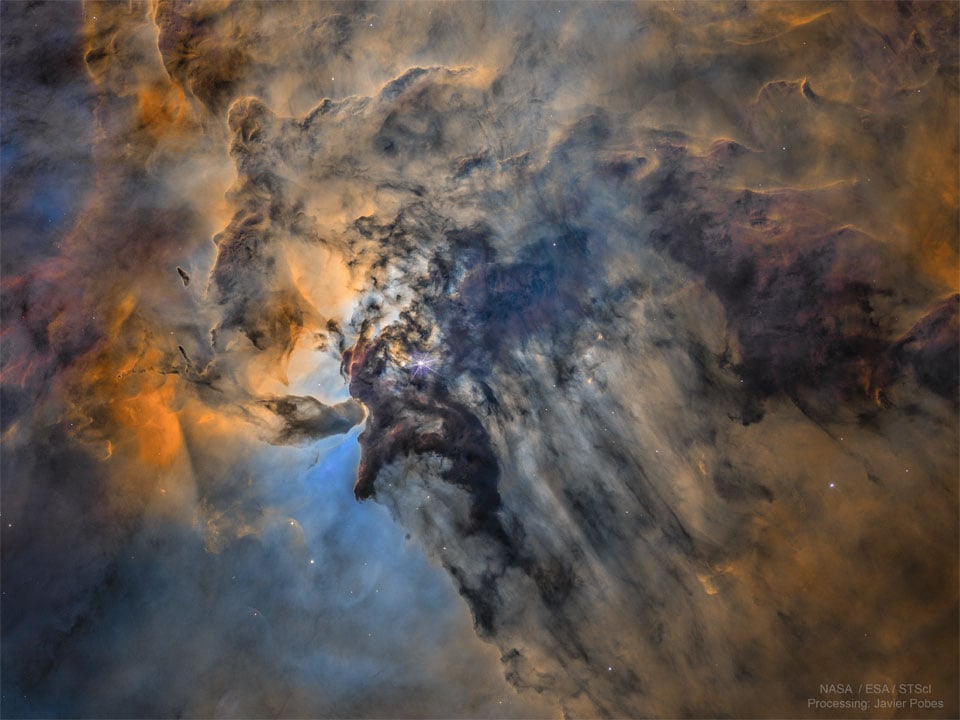 The Busy Center of the Lagoon Nebula
The Busy Center of the Lagoon Nebula
Related Communities
🔭 Science
- !astronomy@mander.xyz
- !curiosityrover@lemmy.world
- !earthscience@mander.xyz
- !esa@feddit.nl
- !nasa@lemmy.world
- !perseverancerover@lemmy.world
- !physics@mander.xyz
- !space@beehaw.org
- !space@lemmy.world
🚀 Engineering
🌌 Art and Photography
Other Cool Links
founded 2 years ago
MODERATORS
you are viewing a single comment's thread
view the rest of the comments
view the rest of the comments
